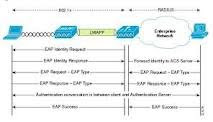
IEEE 802.11i
it requires new encryption key protocols, known as Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). The 802.11i standard was officially ratified by the IEEE in June of 2004, and thereby became part of the 802.11 family of wireless network specifications.
The 802.11i specification offers a level of security sufficient to satisfy most government agencies. However, AES requires a dedicated chip, and this may mean hardware upgrades for most existing Wi-Fi networks. Other features of 802.11i are key caching, which facilitates fast reconnection to the server for users who have temporarily gone offline, and pre-authentication, which allows fast roaming and is ideal for use with advanced applications such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
IEEE 802.11r
Uses a 3-tier mention architecture that divides the access network into mobility zones. A mobility zone is defined as the collection of lightweight access points connected to a central management unit, here after referred to as controller. Generally, neighbouring access points covering a certain geographic zone are grouped into a single mobility zone.
IEEE 802.11k
802.11k is a proposed standard for how a wireless local area network (WLAN) should perform channel selection, roaming, and transmit power control (TPC) in order to optimize network performance.
It uses Radio Resource Management which can enable STAs to understand the radio environment in which they exist. The Radio Resource Management service includes measurements that extends the capability, reliability, and the maintainability of WLANs by providing standard measurement s across vendors, and provides the resulting measurement data to upper layers in the communications stack.
IEEE 802.11w
It is a wireless encryption standard relies on 802.11i framework to protect against subtle attacks on wireless LAN (WLAN) management frames .It also defines enhancements such as data integrity, data origin authenticity, replay protection, and data confidentiality.